Why Teeth Whitening Hurts
Teeth whitening, while a popular cosmetic procedure, can sometimes bring about discomfort. The process involves using bleaching agents to lighten the color of your teeth, and while it can result in a brighter smile, it can also lead to temporary pain or sensitivity. Understanding the reasons behind this discomfort is crucial for anyone considering teeth whitening. The pain experienced during teeth whitening is often related to the ingredients used in the whitening products and how they interact with your teeth and gums. Various factors, including the concentration of the whitening agent, the duration of the treatment, and the individual’s oral health, can influence the level of sensitivity experienced. Being aware of these factors can help you prepare for the procedure and take steps to minimize any potential pain.
Tooth Sensitivity The Main Culprit
Tooth sensitivity is the most common cause of pain during teeth whitening. This sensitivity occurs because the bleaching agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, penetrate the enamel and reach the dentin layer of your teeth. The dentin layer contains microscopic tubules that lead to the tooth’s nerve center. When these tubules are exposed to the whitening agents, they can cause irritation to the nerves, resulting in pain. This sensitivity can manifest as a sharp, shooting pain or a more general ache. The level of sensitivity varies greatly from person to person, and it is often temporary, typically subsiding within a few days after the whitening treatment. The sensitivity is often exacerbated by cold or hot foods and drinks.
Enamel Erosion The Risk

Enamel erosion can exacerbate the sensitivity experienced during teeth whitening. Enamel is the hard, protective outer layer of your teeth. If this enamel is weakened or eroded, the underlying dentin becomes more exposed, making the teeth more susceptible to the effects of whitening agents. Factors such as the frequent consumption of acidic foods and drinks, aggressive brushing, or pre-existing dental conditions can contribute to enamel erosion. When the enamel is compromised, the whitening agents can penetrate the dentin more easily, causing heightened sensitivity and pain. Maintaining good oral hygiene, including using a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoiding excessive consumption of acidic substances, is essential to protect your enamel and minimize the risk of increased sensitivity during whitening.
Gum Irritation During Whitening
Gum irritation is another potential source of pain during teeth whitening. Whitening products can sometimes come into contact with the gums, leading to inflammation or a burning sensation. This irritation is more likely to occur with at-home whitening kits, especially if the trays do not fit properly or the bleaching agent is used excessively. The gums can become red, swollen, and tender, which can cause significant discomfort. Professional whitening treatments often involve protecting the gums with barriers or shields to minimize contact with the whitening agent. If you experience gum irritation, it’s crucial to adjust your whitening routine, such as reducing the treatment duration or frequency, and to ensure that the product is applied correctly to avoid direct contact with your gums. In severe cases, consult with your dentist to address the irritation and adjust your treatment plan.
Chemical Composition of Whitening Agents
The chemical composition of the whitening agents plays a significant role in the potential for pain. The active ingredients, most commonly hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, are designed to break down stains and lighten the teeth. The concentration of these ingredients directly impacts the effectiveness of the whitening process, but it also influences the likelihood of causing sensitivity. Higher concentrations of these chemicals can lead to more intense whitening but also increase the risk of pain and irritation. The pH level of the whitening products can also affect sensitivity; products with a lower pH can be more acidic and potentially more irritating to the teeth and gums. Manufacturers often include additives to help stabilize the active ingredients and reduce sensitivity, but the overall chemical makeup of the product is a key factor in how your teeth and gums will respond to the treatment. Understanding these chemical properties can help you and your dentist select the most appropriate whitening product for your needs.
Hydrogen Peroxide & Its Role

Hydrogen peroxide is a primary active ingredient in many teeth whitening products. It works by penetrating the enamel and breaking down the stain molecules that cause discoloration. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide varies, with professional treatments often using higher concentrations than over-the-counter products. Higher concentrations can deliver faster and more effective whitening results, but they also increase the potential for tooth sensitivity. Hydrogen peroxide can cause the tubules in the dentin to open, allowing the whitening agents to reach the nerves and cause pain. This sensitivity can range from mild to severe, depending on the individual’s tooth sensitivity, the concentration of the hydrogen peroxide, and the duration of the treatment. It is crucial to follow the instructions provided with the whitening product to minimize the risk of pain and irritation. Your dentist can assess your teeth and recommend the appropriate concentration of hydrogen peroxide for your specific needs.
Carbamide Peroxide The Alternative
Carbamide peroxide is another common bleaching agent used in teeth whitening. It breaks down into hydrogen peroxide when it comes into contact with water. Carbamide peroxide is often used in at-home whitening products, such as trays and strips, and it typically has a lower concentration than hydrogen peroxide used in professional treatments. While less potent than higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, carbamide peroxide can still cause sensitivity. The slow release of hydrogen peroxide from carbamide peroxide allows for a more gradual whitening effect, which some individuals may find more comfortable. The overall impact on sensitivity depends on the specific formulation of the product, the length of time it is used, and the individual’s dental health. Consulting with your dentist can help you decide whether carbamide peroxide is the right choice for your teeth whitening needs and to ensure you use it safely and effectively.
Factors Influencing Sensitivity
Several factors influence the level of sensitivity experienced during teeth whitening. Individual tooth sensitivity is a major determinant, with some people naturally having more sensitive teeth than others. The concentration of the whitening agent is another critical factor, with higher concentrations generally leading to more sensitivity. The duration of the treatment, or how long the whitening agent is in contact with your teeth, can also affect sensitivity; longer exposure times can increase the likelihood of pain. Oral hygiene habits, such as how frequently you brush and floss, can also influence the sensitivity level. Poor oral hygiene might weaken enamel, making your teeth more susceptible. Pre-existing dental conditions, such as cavities or gum disease, can also exacerbate sensitivity. A thorough assessment of these factors will help you anticipate potential sensitivity and take preventive measures.
Individual Tooth Sensitivity Levels

Individual tooth sensitivity levels vary widely, influencing how people react to teeth whitening. Some individuals have naturally more sensitive teeth due to thinner enamel or larger dentin tubules. These individuals are more likely to experience pain during the whitening process. Others might have no sensitivity at all, or only a mild amount. Factors like genetics, age, and dental history can influence tooth sensitivity. For example, people with a history of dental work, such as fillings or crowns, might experience more sensitivity around these areas. Likewise, those with receding gums might have more exposed root surfaces, which can be extra sensitive. Dentists can evaluate your sensitivity levels before starting a whitening treatment. This will allow them to adjust the treatment plan to minimize your discomfort, possibly through the use of lower concentrations of bleaching agents or desensitizing products.
Whitening Product Potency
The potency of the teeth whitening product plays a significant role in the level of sensitivity experienced. Professional teeth whitening treatments performed by dentists generally use higher concentrations of hydrogen peroxide than over-the-counter products. While these higher concentrations can produce faster and more dramatic whitening results, they also increase the potential for tooth sensitivity. At-home whitening kits, available at drugstores, usually contain lower concentrations of either hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These products may cause less sensitivity but might require longer usage periods to achieve desired results. The potency of the product is often reflected in its instructions, which provide guidelines on the duration of use and frequency of application. Following the product instructions carefully is crucial to minimize sensitivity and prevent any potential complications. Choosing the right potency level often involves a trade-off between the speed of whitening and the potential for discomfort.
Pre-Existing Dental Conditions
Pre-existing dental conditions can influence how your teeth respond to teeth whitening. Cavities, gum disease, and cracked teeth can significantly increase the risk of sensitivity during and after the whitening process. If you have cavities, the whitening agents can penetrate the tooth more easily, reaching the nerves and causing pain. Gum disease can lead to inflamed gums, making them more sensitive to the chemicals in whitening products. Cracked teeth can also provide pathways for the whitening agents to reach the nerve. Before undergoing teeth whitening, your dentist should perform a thorough examination to identify and address any pre-existing dental issues. Treating these conditions before whitening can help reduce sensitivity and ensure a safer and more comfortable experience. Failure to address these problems beforehand can lead to complications, including increased pain and potentially worsening dental problems.
Managing Teeth Whitening Pain
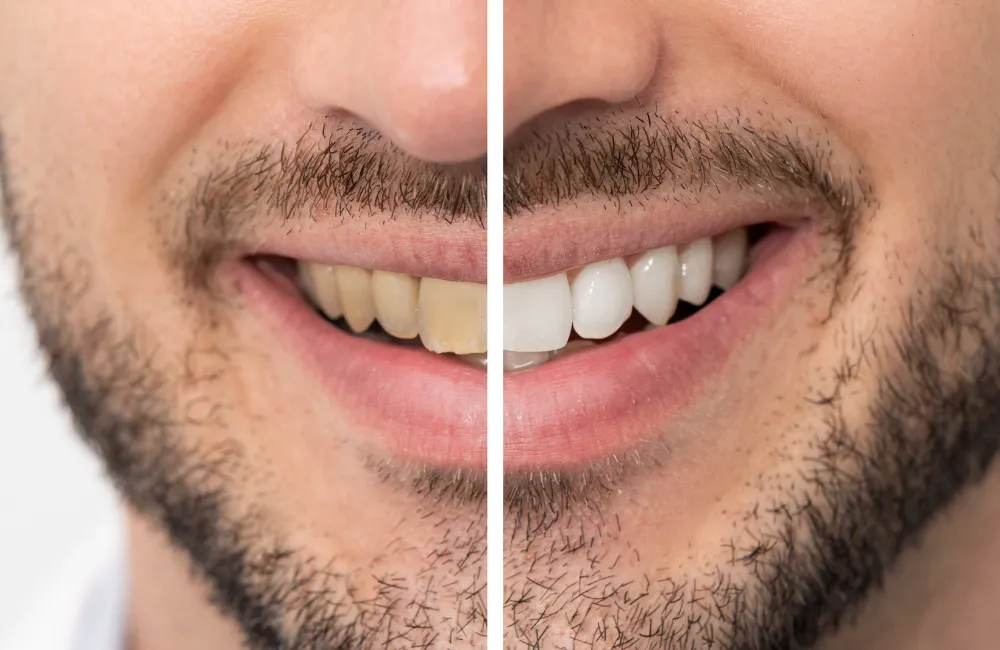
There are several strategies to manage teeth whitening pain. Using a desensitizing toothpaste containing potassium nitrate can help block the tubules in the dentin, reducing nerve irritation. This type of toothpaste should be used for a couple of weeks before starting the whitening treatment and during the whitening process. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate mild to moderate pain. Avoiding acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits, soda, and coffee, can also help minimize sensitivity. These foods can erode the enamel and increase sensitivity. Following your dentist’s instructions regarding the application of the whitening product is also essential. Using too much product or leaving it on for longer than recommended can increase the risk of pain. If you experience severe pain, contact your dentist for further guidance. They may adjust your treatment plan or recommend other solutions to reduce discomfort.
Over-the-Counter Whitening Products
Over-the-counter (OTC) teeth whitening products are readily available and can be a convenient option for improving the brightness of your smile. These products typically contain lower concentrations of bleaching agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, compared to professional treatments. Common OTC options include whitening strips, trays, and toothpastes. Whitening strips are easy to use and adhere directly to the teeth, delivering the whitening agent. Whitening trays involve filling custom or pre-made trays with a whitening gel and wearing them for a specific duration. Whitening toothpastes contain mild abrasives and whitening agents to remove surface stains. While OTC products can be effective, they might cause some level of sensitivity. The lower concentration of bleaching agents often means slower results and a lower risk of significant pain. If you experience sensitivity, it’s essential to follow the product instructions carefully, avoid overuse, and consider using desensitizing toothpaste. Consulting with your dentist before using any OTC whitening product can provide guidance and help you choose the best option for your teeth and oral health.
Professional Dental Whitening Treatments
Professional dental whitening treatments offer several advantages, including faster results and often a more controlled approach to minimize sensitivity. These treatments are performed by dentists, who have access to stronger bleaching agents and can tailor the treatment to your specific needs. In-office whitening typically involves applying a high-concentration hydrogen peroxide gel to the teeth, which is then activated using a special light or laser. The dentist will monitor your progress and can adjust the treatment as needed to manage any sensitivity. Professional whitening treatments often include gum protection measures to reduce gum irritation. Custom-fitted trays for at-home whitening can be used in conjunction with in-office treatments to maintain the results and further lighten your teeth. Although professional treatments can cause sensitivity, your dentist can provide strategies to minimize discomfort, such as using desensitizing agents or adjusting the concentration of the bleaching agent. Choosing professional whitening ensures that the treatment is performed safely and effectively, with the guidance of a dental professional.
Desensitizing Toothpaste The Solution
Desensitizing toothpaste is a valuable tool for managing tooth sensitivity during teeth whitening. These toothpastes contain active ingredients, such as potassium nitrate or stannous fluoride, which help block the pathways to the tooth’s nerve endings. Potassium nitrate works by penetrating the dentin tubules and reducing the nerve’s response to stimuli, such as the whitening agents. Stannous fluoride helps to block the tubules and also strengthen the enamel, making the teeth less sensitive. To maximize the effectiveness of desensitizing toothpaste, you should start using it a few weeks before beginning teeth whitening and continue using it throughout the whitening process. Brushing twice daily with a desensitizing toothpaste can significantly reduce sensitivity and make your whitening experience more comfortable. For best results, use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid further enamel abrasion and follow your dentist’s recommendations for oral hygiene.
Avoiding Pain Before and After Whitening
Preparing for teeth whitening can significantly minimize the likelihood of experiencing pain. Before starting any whitening treatment, it’s essential to consult with your dentist. They will examine your teeth to identify any pre-existing dental conditions, such as cavities or gum disease, and address them. Using a desensitizing toothpaste for a few weeks before whitening can also help reduce sensitivity. During the whitening process, follow all instructions carefully, including the recommended duration and frequency of treatments. After whitening, avoid consuming acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits, soda, and coffee, as these can increase sensitivity. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush gently to avoid enamel abrasion. Continuing to use desensitizing toothpaste after whitening can provide ongoing relief. By taking these proactive steps, you can increase the chances of a comfortable and successful teeth whitening experience. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are essential for maintaining the results and overall dental health.
Proper Application Techniques
Proper application techniques are crucial to minimize pain and maximize the effectiveness of teeth whitening treatments. When using at-home whitening products, such as trays or strips, it’s essential to carefully follow the instructions provided. Ensure that the whitening agent is applied evenly to the teeth and that the tray fits snugly without spilling the gel onto your gums. If you are using strips, be sure to apply them correctly, ensuring they adhere properly to the teeth surface and avoid contact with the gums. Overfilling trays or using excessive amounts of the whitening agent can increase the risk of gum irritation and sensitivity. In professional treatments, the dentist will apply the whitening agent carefully, often using gum shields or barriers to protect the gums from the bleaching chemicals. Following these proper application techniques ensures a safe and effective whitening experience, reducing the potential for pain and achieving the desired results.
Avoiding Acidic Foods and Drinks

Avoiding acidic foods and drinks before and after teeth whitening can significantly reduce sensitivity and maintain the results. Acidic substances, such as citrus fruits, soda, coffee, and certain juices, can erode the enamel, making your teeth more susceptible to the effects of the whitening agents and increasing sensitivity. Before starting a whitening treatment, consider reducing your intake of these items. After whitening, it’s crucial to avoid them for a few days or even weeks, as your teeth are more vulnerable during this period. Opt for a balanced diet that includes calcium-rich foods, which can help strengthen your enamel. Drinking water can also help to neutralize the acidity in your mouth and protect your teeth. By being mindful of your diet, you can support your teeth whitening efforts and minimize any discomfort.
Post-Whitening Care
Post-whitening care is essential to maintain the results of your teeth whitening treatment and to minimize any discomfort. After the procedure, avoid consuming highly pigmented foods and drinks, such as red wine, berries, and dark sauces, for a few days or weeks to prevent staining. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is critical. Brush your teeth gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush twice a day, using a desensitizing toothpaste if you experience sensitivity. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also necessary to maintain your oral health and to keep your teeth bright. You may also want to consider touch-up treatments at home or in the dental office, as needed, to maintain your desired level of whiteness. By following these post-whitening care tips, you can prolong the life of your results and keep your smile radiant.
When to Seek Professional Help
While some sensitivity is common during teeth whitening, it’s important to know when to seek professional help. If you experience severe or persistent pain that doesn’t subside after a few days, it’s best to consult with your dentist. Similarly, if you notice any signs of complications, such as excessive gum irritation, blisters, or changes in the appearance of your teeth, schedule an appointment. These symptoms could indicate a problem with the whitening treatment or an underlying dental issue that needs to be addressed. Your dentist can assess the situation, determine the cause of the pain, and recommend appropriate solutions. They may adjust your treatment plan, provide desensitizing treatments, or address any underlying dental problems that are contributing to the discomfort. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help if you have any concerns or questions about the teeth whitening process.
Persistent Pain

Persistent pain after teeth whitening is a sign to seek professional evaluation. If the sensitivity or discomfort doesn’t subside within a few days after stopping the whitening treatment, it could indicate a problem. Prolonged pain might be caused by the high concentration of the whitening agents, the exposure of the dentin, or pre-existing dental conditions. Your dentist can examine your teeth and gums to identify the source of the pain and determine the best course of action. This might involve desensitizing treatments, such as fluoride applications or the use of special toothpastes. They can also assess whether any underlying dental issues, such as cavities or gum disease, need to be addressed. Ignoring persistent pain can lead to complications and potentially worsen the problem. Timely intervention by a dental professional ensures the proper management of the pain and the preservation of your oral health.
Signs of Complications
Being aware of the signs of potential complications during and after teeth whitening is essential. Excessive gum irritation, characterized by redness, swelling, or blisters, could be a sign that the whitening agent is irritating your gums. Changes in tooth appearance, such as increased translucency, could indicate enamel erosion. Pain that is severe or persists for an extended period also warrants concern. If you notice any of these signs, it is crucial to contact your dentist immediately. Early intervention can prevent complications and protect your oral health. Your dentist can assess the situation, provide appropriate treatment, and adjust your whitening plan if needed. Ignoring these signs can lead to more serious dental problems. Regular dental check-ups can also help identify and address any potential issues before they escalate, ensuring a safe and successful teeth whitening experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while teeth whitening can be an effective way to enhance your smile, it’s important to understand why it might cause pain and how to manage it. Tooth sensitivity is the most common side effect, which is often related to the interaction of whitening agents with the enamel and dentin. Factors such as the concentration of the bleaching agent, individual tooth sensitivity, and pre-existing dental conditions can all influence the level of discomfort experienced. By understanding these factors, using appropriate pre- and post-whitening care, and consulting with your dentist, you can minimize the risk of pain and achieve a brighter, healthier smile. Proper application techniques, careful product selection, and a commitment to good oral hygiene are key to a successful and comfortable teeth whitening journey. Always prioritize your dental health by seeking professional guidance when necessary.